The Psychology of Emotion
Emotions
Where Do Our Emotions Come From?
What Are Emotions?
There is the science of emotions, and there is the feelings of emotions. Neuroscience has studied how brains generate emotions. Philosophers have debated the causes of emotions.Psychologists have studied the many aspects of emotions and its impact on our behavior.
Many professionals in the field of psychology believe our emotions are inter-related to the way we interpret the world. How we look at things, evaluate events, and weigh the significance of the experience will determine how we react. Will we be happy, angry, glad or sad? If someone says something to you, how you respond is a reflection of the meaning you impart on their words.
It is because of the varying and sometimes unpredictable response that we humans have to each encounter, that makes defining emotions very complex.
Emotions can be considered the result of an interaction between an automatic ingrained, unconscious process, and purposeful, conscious, and deliberate reactions, combined with internal sensations.
The amygdala plays a major role in our emotions, more than any other part of our brain.
Emotions is a very big topic, but generally it can be defined by the positive and negative feelings that are a reaction to events and experiences.
The Psychology of Emotions
There are many theories about emotions. Some say an emotion has a thinking part, a judicious part, a physical part, and an unconscious part. With every emotional response, there are behavioral, hormonal, and autonomic reactions. Autonomic responses allow for a quick reaction to gather our energy, and react quickly o a situation. Our body reacts physically to our emotions, from increasing our heart rate, to providing glucose energy to our muscles, and many more physical reactions. We also have behaviors that communicate our emotional feelings to others, such as gestures, facial expressions, and other non verbal cues.
In the 1800’s two psychologists, independently arrived at he same conclusion about emotions. They concluded that emotions produced a physiological response, which brought
about certain behaviors, which gave the brain feedback that makeup our feelings of emotions. Most people think that they directly feel their emotions from their experiences. Walter Cannon, disagreed with this theory to be incorrect. He believed that our internal organs were not sensitive enough, nor could they react quick enough to the emotions we feel.
Emotions and feelings are tied together. Emotions can be separated from mood. Mood is a state of mind that can last for hours, days, weeks or any lengthy period of time. An emotion is an almost instantaneous reaction to an experience, a thought, a memory, an event, an interaction.
Understanding Our Emotions
Emotions and Our Thoughts
Philosophers try to explain what causes these emotions, that our thoughts precipitate our emotions. Emotions can trigger our thoughts and are activated by our thoughts. Emotions can only be activated where there is an understanding. For example, if you hear a dentist’s drill, you might become fearful because the drill triggers thoughts of painful dental work. If you didn't know what a drill is, when you heard the sound, you wouldn't be anxious, because a dentist’s drill has no meaning to you.
The emotion will only present itself when someone understands the situation. Emotion, therefore, comes from our beliefs. We react to what we believe. Our emotions come out automatically, we don’t prethink or go through full thought processes to elicit the emotion. If we are concerned we might be bitten by a dog, it is better to have the fear emotion kick in quickly so we can run, than to wait for the dog to attack.
We are responding to a previous belief and judgment. Sometimes, because of this, our response may not be appropriate, if our original belief was flawed. Someone might be afraid of dogs, because dogs can bite. But not all dogs bite. Seeing any dog, triggers a sense Emotions need to be evaluated to make sure they are based on the correct belief. Otherwise, we may not be guided by the correct emotional response.
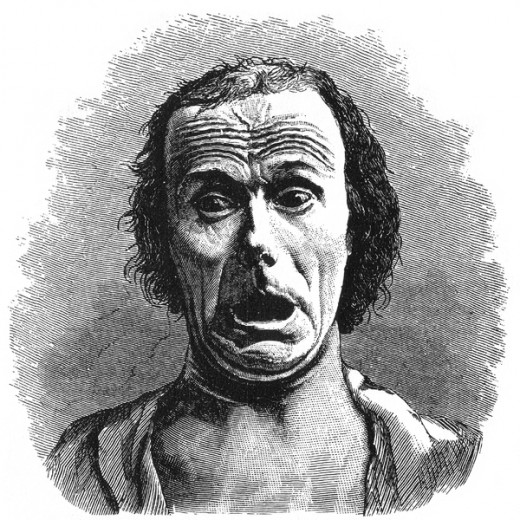
Duchenne Photos Used by Darwin

Emotions and Evolution
Emotions are a complicated aspect of our personality and psychology. Emotions send us signals to react, to relax, to trust, to be vigilant. We are guided by our emotions on almost every judgment and decision we make. There is so much history to our emotions. We gain many of our beliefs and concepts by what is taught to us. Emotions help us feel, and imagine, and take action.
Our faces have approximately 90 muscles, 30 are dedicated to signaling our emotions to other humans. We watch people for their expressions. If they look angry we may not approach them. If they look sad, we may ready ourselves to comfort them. We respond and connect with others through the bond of emotions.
Sometimes when someone else has a reaction, it triggers an emotion in us, one that we may not have realized that it was that deep inside us. Sometimes we react to someone else, because we haven’t dealt with our own emotions, and in essence, by helping them, we are trying to help ourselves.
Emotions are designed to help us survive. That is why, of the 6 basic emotions, there are more negative, than positive emotions.
Emotions have been debated by philosophers, scientists, and psychologists throughout time. Charles Darwin, the father of evolution, did a study in 1868, to prove that people and animals have a natural and universal set of expressions that depict our emotions, and can understand each other’s feelings.
The results of Darwin’s experiment has made a great contribution to psychology. Darwin surveyed people about 11 photographs of an old toothless man who had different contorted facial expressions, asking them what emotion the man was feeling.
Darwin wanted to prove that human beings have basic emotions that other people can pick up from each other. Darwin wrote a book from this experiment called, The Expression of Emotions in Man and Animals. In his writing he states that these emotions are experienced by animals too, and helps us develop a kindred spirit with other species.
Emotions and Psychology
In 1972, an anthropologist named Paul Ekman, tried to disprove Darwin’s research. He ended up confirming what Darwin had concluded and described 6 basic emotions that all humans experience across cultures and throughout the world. These emotions are believed to be the basis of all emotions people feel.
- surprise
- fear
- happiness
- sadness
- anger
- disgust or contempt
Ekman and his peers used facial reactions that are considered universal tocome up with these six. Scientists believe the majority of animals experience these same emotions. Some theorists believe these basic emotions are the foundation for more complex emotions that higher functioning species experience.
The lesson from both Darwin and Ekman is that our ability to understand another’s emotion, whether man or animal, makes us more humane, and more kind, more human.
Emotions are difficult to quantify, to define, to measure. Yet, by merely observing and with few words expressed, we can know so much about what someone else is feeling.
The Four Parts of Human Emotions
Human emotions, it is generally believed have 4 parts:
- Cognitive Reactions derived from our perceptions, our thoughts, our memories, and our experiences
- Affect - the emotional, tone, mood and feeling, tone and mood to a thought.
- Physiological Reaction - our emotionsl trigger hormones that raise our blood pressure, speed up our heart rate, increase our metabolism, and cause other changes in our brain and body.
- Behavioral Responses - motivates an expression of our feelings, and causes certain behaviors to come out. It is shown in our body language, our facial expressions, and overt feelings like crying and screaming.
All emotions are of 2 types - either negative or positive. Considering evolution, emotions are derived from 3 main functions:
- for survival and adaptation
- regulation and our perception of the world and to recall memories
- communication to relay our needs and feelings to others
We express and recognize a large array of emotions in a variety of intensity.
The Study of Human Emotions
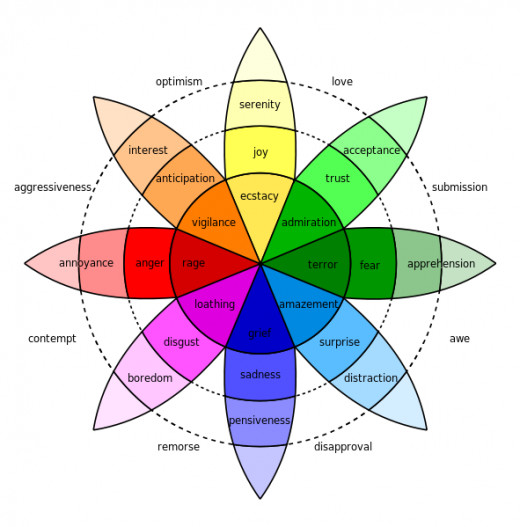
In 1980, Robert Plutchik, a psychologist at the Albert Einstein School of Medicine in New York, described 8 main emotions of humans that are associated with adaptive behavior.
He believes that these are innate, and come about early in human development. He set up 8 opposites that he called Plutchik’s Wheel of Emotions.
According to Robert Plutchik (1980), there are eight primary human emotions that relate to adaptive behavior. It is believed that these are innate or develop early on due to their survival values.
Plutchik came up with the wheel of emotion to show how our many emotions are inter-related.
Emotions have served an evolutionary purpose by helping s survive. When we encounter danger, it is our automatic emotional response that helps us get out of harms way and avoid dangers. We share basic emotions with other animals, but additionally developed a more complex system of rationalization, and an ego. Our ability to reason about ourselves helps shape our world, our future, and dominate other species.
Putchik Wheel of Emotion
Humanity and Emotions
Some people become overloaded with emotions, which can cause anxiety, and other emotional problems. Reasoning helps us deal with emotions.
Emotions also help us build relationships, bond with others, and fit in society. Emotions help us to know love and joy, sadness, and compassion. We fear and trust and gain a sense of pride from our emotions.